A condensing boiler is a system that uses a highly efficient condensing heat recovery device to absorb both the sensible heat and the latent heat released during the condensation of water vapor from the high-temperature flue gases emitted by the boiler. This process significantly improves the boiler's thermal efficiency.
The key technology behind a condensing boiler is the condensing process, which is a modern, energy-saving, and environmentally friendly method. The principle is straightforward: it recovers heat energy from flue gases through condensation.
In traditional boilers, the flue gas temperature is usually between 160°C and 250°C or even higher. This causes the water vapor generated during fuel combustion (e.g., methane combustion: CH₄ + 2O₂ → CO₂ + 2H₂O) to remain in a superheated state and escape with the flue gases. As a result, the thermal efficiency of traditional boilers is generally only 85% to 91%. In contrast, a condensing gas boiler reduces the flue gas temperature to below 58°C, fully recovering both the sensible heat and the latent heat released during the condensation of water vapor. This allows the thermal efficiency to reach up to 109%.
The core of a condensing gas boiler is its ability to recover heat from high-temperature flue gases. Typically, the flue gas temperature after combustion is around 140°C. By using a condensing system, this temperature can be reduced to approximately 60°C. This process increases thermal efficiency by about 10%, thereby saving roughly 10% on gas consumption. Additionally, during energy recovery, harmful gas emissions are reduced, minimizing environmental pollution.
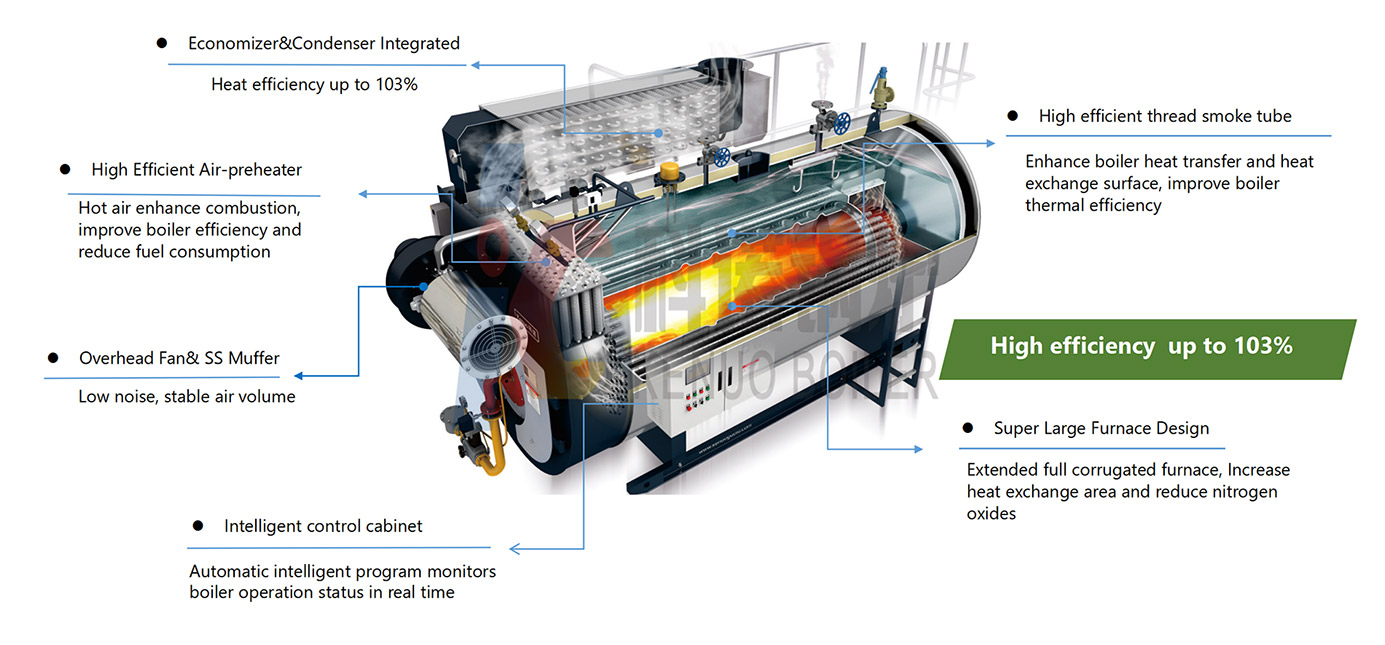
In conventional boilers, the flue gas temperature is generally around 140°C, which leads to significant heat loss. Condensing boilers, on the other hand, utilize condensing technology to lower the flue gas temperature to below 58°C. This causes part of the water vapor in the flue gas to condense into liquid, releasing latent heat during the phase change. This recovered heat, previously lost with the flue gases, contributes to the boiler's increased thermal efficiency.
When calculating the thermal efficiency of boilers, the latent heat carried away by high-temperature flue gases is typically not considered. However, condensing boilers effectively utilize this latent heat, allowing their thermal efficiency to exceed 100%. The theoretical maximum thermal efficiency of a condensing boiler can reach 111%.
With its high efficiency, energy-saving, and environmentally friendly features, the condensing boiler excels in reducing gas consumption, improving thermal efficiency, and lowering pollutant emissions. As environmental and energy policies advance, condensing boilers are expected to play a crucial role in the future of the boiler industry.
Kenuo adheres to the core principles of efficiency, energy conservation, and environmental protection, dedicating itself to the in-depth research of condensing boilers tailored to diverse customer operating conditions. Its core products include:
Through continuous innovation, Kenuo is committed to providing customers with high-quality boiler products and services.